What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Learn symptoms, causes and treatments
The body’s nervous system is made up of two parts. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) which is composed of the nerves running from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body (the arms and hands, legs and feet, internal organs, joints and even the mouth, eyes, ears, nose, and skin).

01
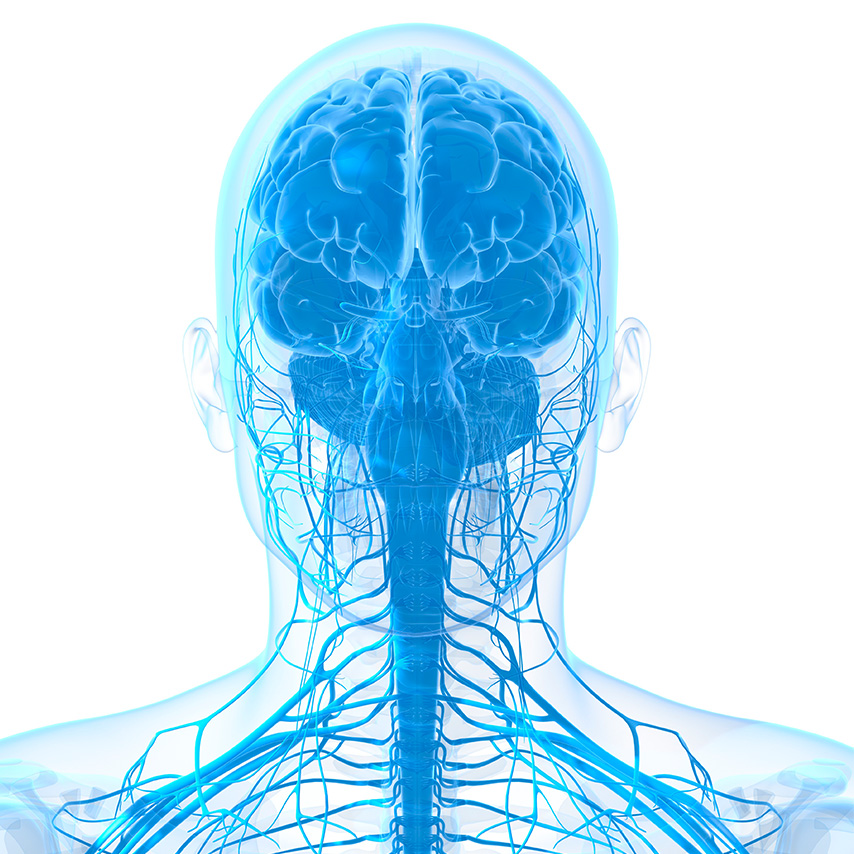
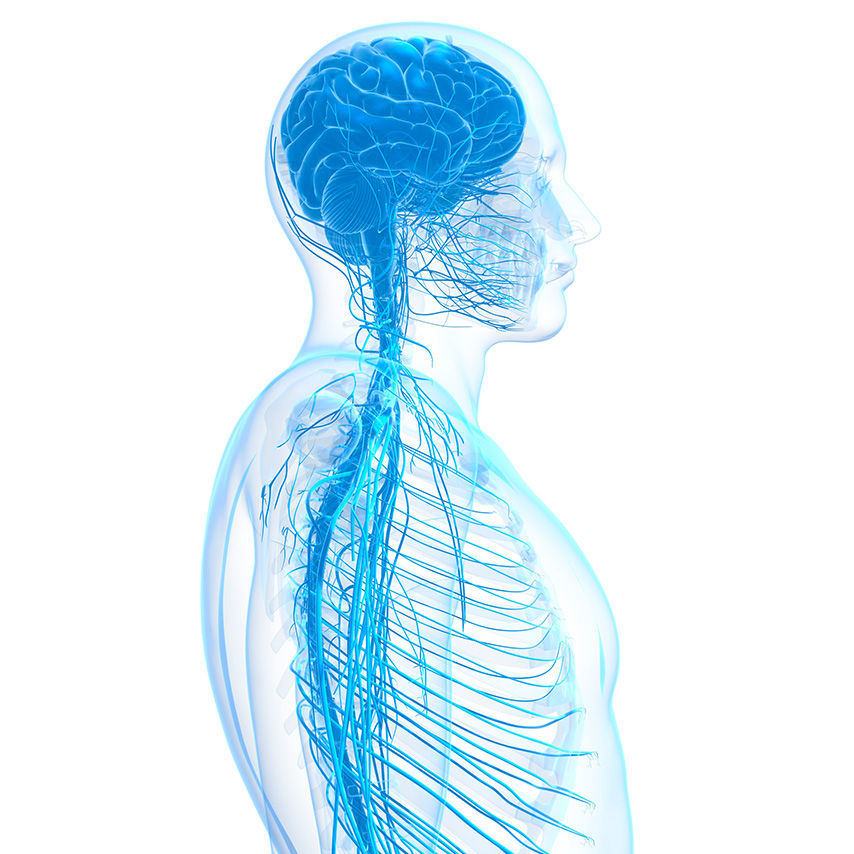
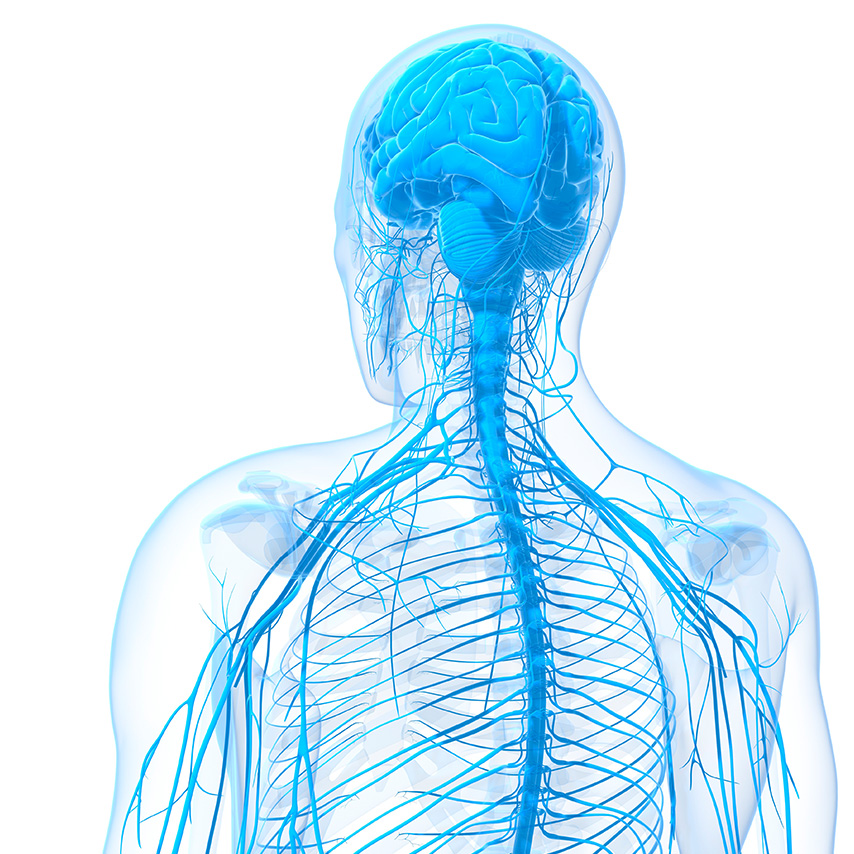
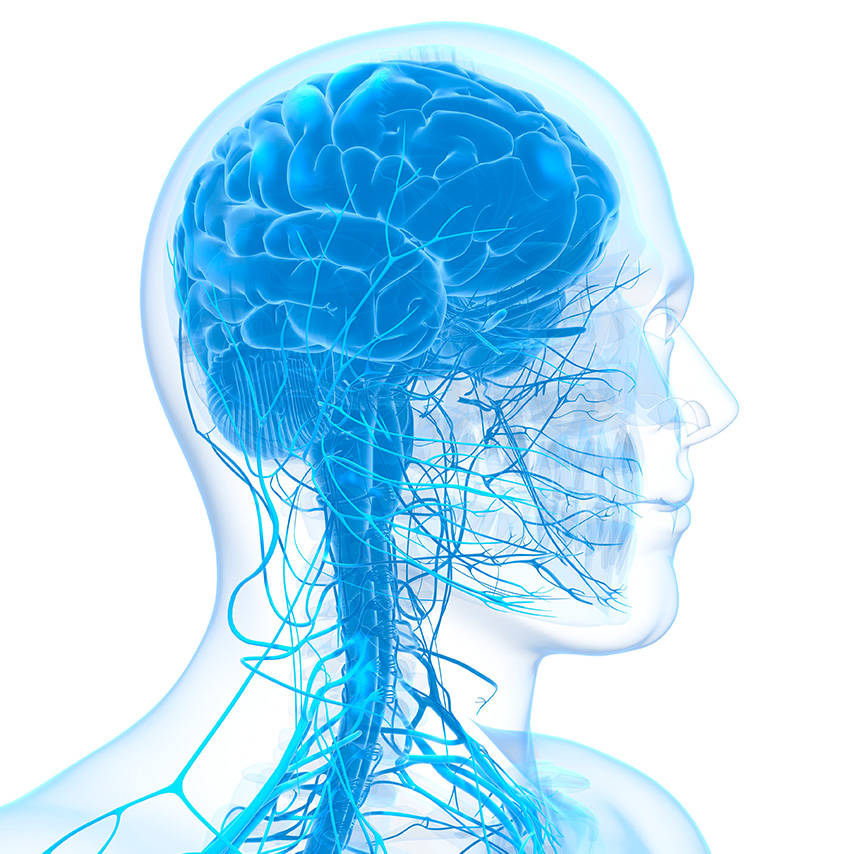
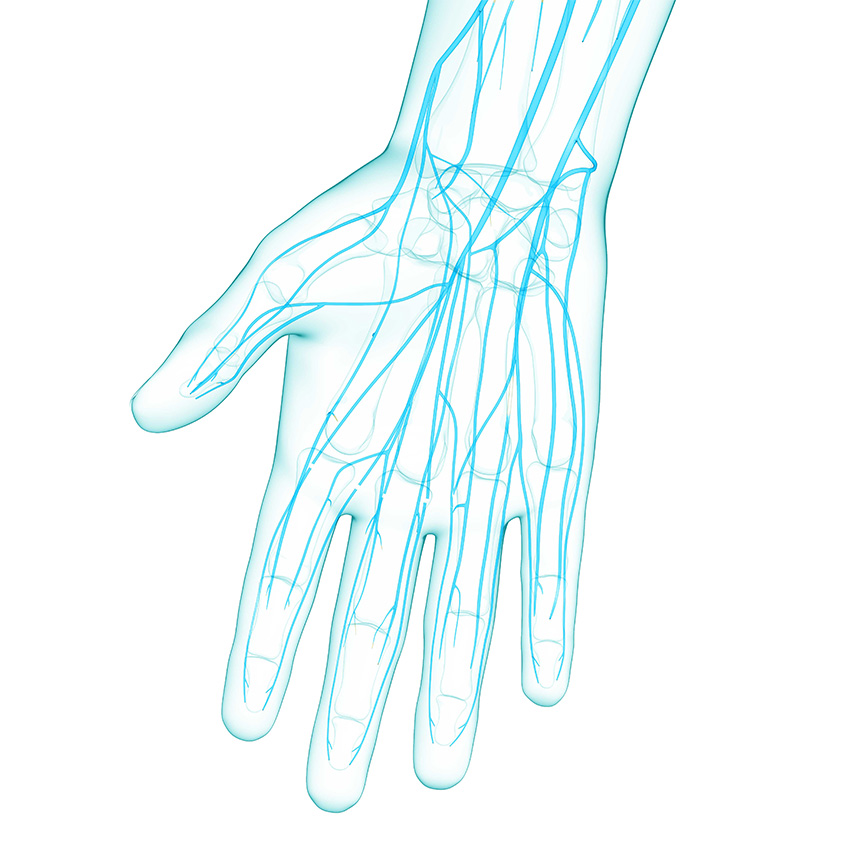
The nervous system
Cranial nerves
Cranial nerves go from your brain to your eyes, mouth, ears, and other parts of your head. Usually, for anatomical reasons the olfactory and optic nerve are not considered part of the PNS but of the CNS (in fact, for example, the optic nerve is involved in a disease of the central nervous system such as multiple sclerosis, which is not a peripheral neuropathy).
Peripheral nerves
Peripheral nerves go from your spinal cord to your trunk and limbs, including hands and feet. They are responsible for what we call somatic functions, including sensation and motor control.
Autonomic nerves
Autonomic nerves go from your spinal cord to your lungs, heart, blood vessels, stomach, intestines, bladder and sex organs. They are responsible for bodily functions such as blood pressure control, sweating and bowel movements among others…
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy occurs when peripheral nerve(s) is/are damaged. The message coming from the periphery (sensation) and going towards the brain can be altered: in this case sensory loss or pain can be present. If the message cannot go from the brain to the periphery (e.g., muscles) weakness will be there. Moreover, as stated above, some components of the PNS are responsible for involuntary functions (e.g., sweating, bowel movements, …); these functions might be altered too.
Peripheral neuropathy is not a single disease. It’s a general term for a series of disorders that result from damage to the body’s peripheral nervous system.
Peripheral neuropathy can affect multiple nerves (polyneuropathy) or only one nerve (mononeuropathy) or nerve group (multiple mononeuropathies) at a time.
Mononeuropathy
Mononeuropathy is usually the result of damage to a single nerve or nerve group by trauma, injury, local compression, prolonged pressure, or inflammation.
Examples include:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: a painful wrist and hand disorder often associated with repetitive tasks on a computer keyboard
- Cubital tunnel syndrome: a painful condition of the hand due to entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the elbow
- Bell’s palsy: a facial nerve disorder
- Meralgia paresthetica: a painful condition of the thigh related to nerve impingement at the inguinal canal
Common Causes of Peripheral neuropathy
There are over 100 known causes of PN. The most common include diabetes, idiopathic neuropathy and chemo-induced neuropathy. Idiopathic neuropathy is when the cause cannot be determined even after extensive testing.

Symptoms
Peripheral neuropathy can usually be detected by numbness and tingling in toes and fingers. Read more about how you can identify peripheral neuropathy.

Treatments
Depending on levels of pain, treatment of PN can vary by individual. Learn what to consider when weighing treatment options.
How to be your own health care advocate
Here are some tips to help you get ready for your appointment and to know what to expect.